An avulsion injury is a serious injury that occurs when a soft tissue is forcibly torn away, either partially or completely. The organ commonly affected by this kind of injury is the skin. Medically speaking, an avulsion injury usually refers to surface trauma where all skin layers have been torn away, thus uncovering its underlying structures, such as, subcutaneous tissue, muscle, tendons, or even bones. It is likened to an abrasion, except in its more severe form, as body parts can be partially or fully detached from the body. Avulsion injury is typically caused by trauma.
Types of Avulsion Injury
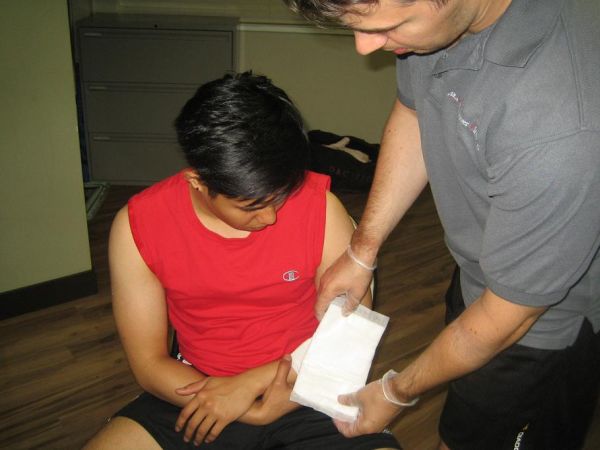
Applying dressing and gauze is usually recommended in wounds, such as those seen in avulsion injuries
There are different types of avulsion injury. These types are the general locations where an avulsion injury can occur, which include:
- Skin (most common)
- Ear
- Eyelid
- Nail
- Tooth
- Nerve (brachial plexus)
- Periosteal
- Surgical
Causes of Avulsion Injury
There are many possible causes for an avulsion injury. These are usually by severe trauma to the skin:
- Human and animal bites
- Gunshot wounds
- Stab wounds
- Crush injuries
- Falls, especially those against jagged surfaces
- Severe burns
- Motor vehicular collisions and accidents, especially those involving dragging incidents
Signs and Symptoms of Avulsion Injury
The signs and symptoms of any avulsion injury is dependent on the location and the nature of the injury
- Minimal to severe bleeding
- Puncture wounds
- A body part may be partially or completely removed
- Mild to severe pain
- Crushed body tissue
First Aid Management for Avulsion Injury
First aid treatment and management will depend on the type of avulsion injury. However, the utmost priority is to reduce pain and discomfort of the patient. The following is the general recommendation in cases of avulsion injury:
- If the patient is unconscious, check for the patient’s airway, breathing and circulation. If necessary, initiate CPR. Call localemergency number.
- For small wounds where there is no damage to structures such as nerves, blood vessels and the like, wash the wound with water and soap. Pat it dry with a clean towel. Apply antibiotic ointment. There is no need to cover the wound.
- For large wounds with bleeding, control bleeding by applying direct pressure on the wound until bleeding stops. Use a clean dressing or any absorbent cloth. If the cloth is soaked with blood, another absorbent cloth on top of the used cloth. Elevate the injured area.
- In cases of stab wounds, do not remove the knife as this maycause more bleeding.
- In cases of amputations, rinse the amputated body part and remove any dirty material that can cause contamination. Wrap the severed part in a clean, damp cloth and place inside a sealed plastic bag before placing inside a bag of cold water.
To learn how to manage an avulsion injury, enroll in First Aid Courses and CPR Training.
Online Sources: